PID Control
A simple PID controller and a visual testbench written in python
Goal:
Provide a tool to quickly visualize and understand the concept behind a model PID controller
Scope:
PID control of a second order linear system with damping under the influence of external forces
Features:
Adjust process parameters to model different second order systems
Adjust PID parameters to observe resulting effects on the controlled system
Visualize the PID control output and its effects on the plant under test
Use cases:
Analyse the stability of model PID systems under a variety of conditions
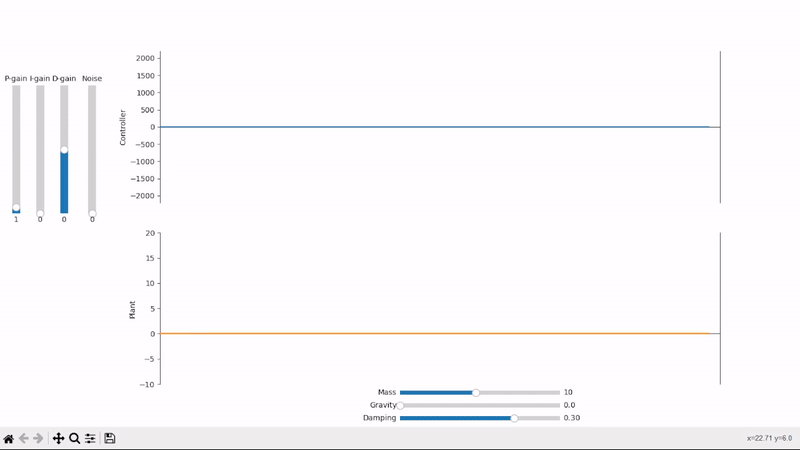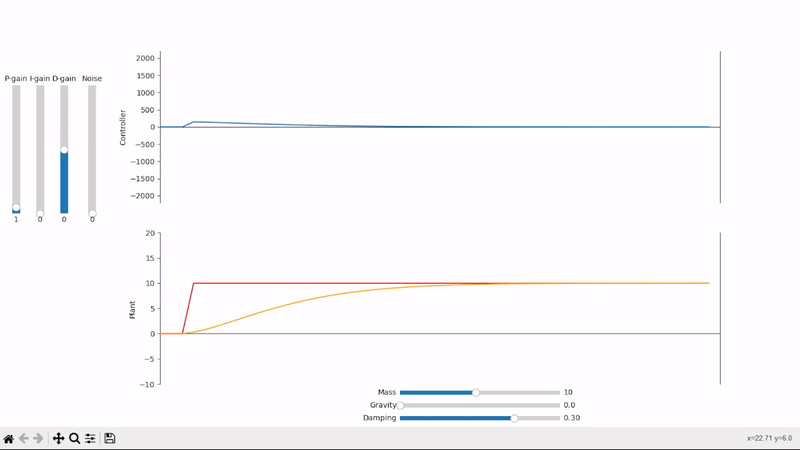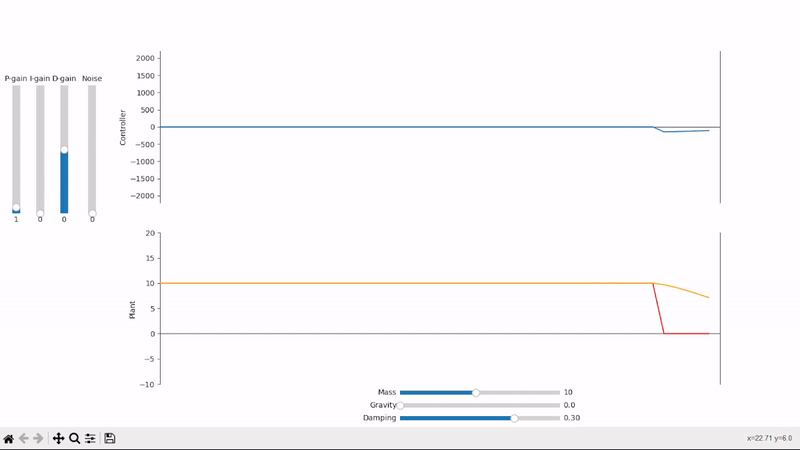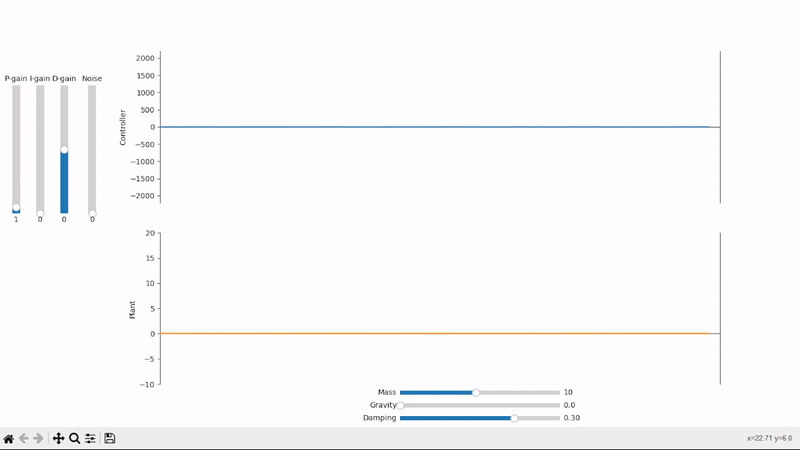
A small amount of proportional gain slowly drives the plant towards the desired setpoint
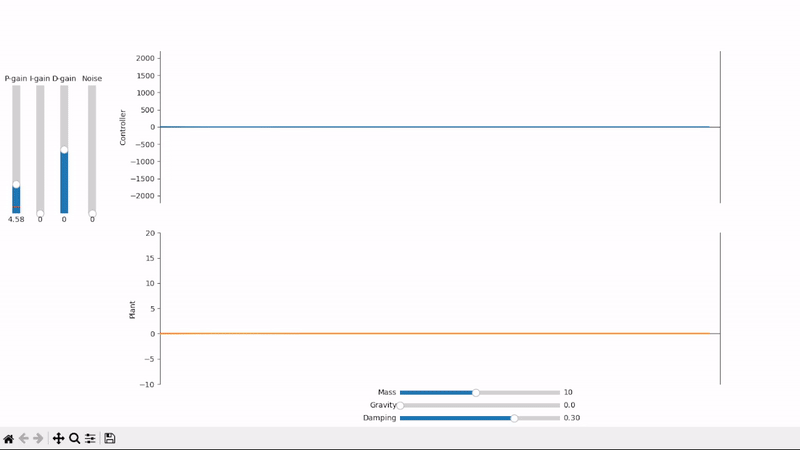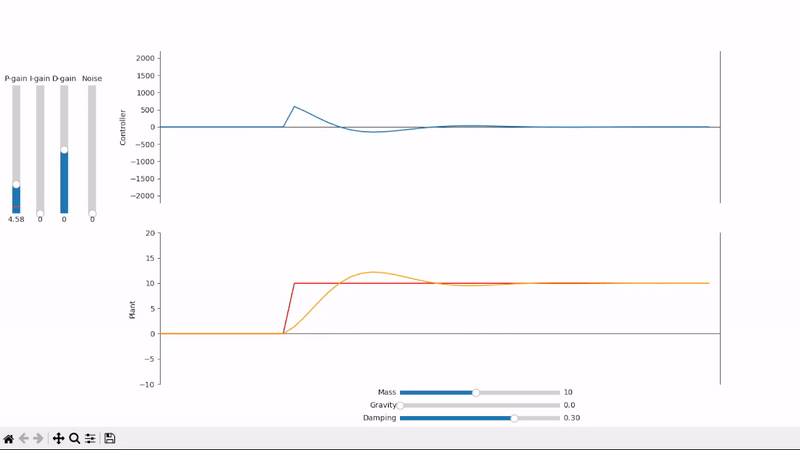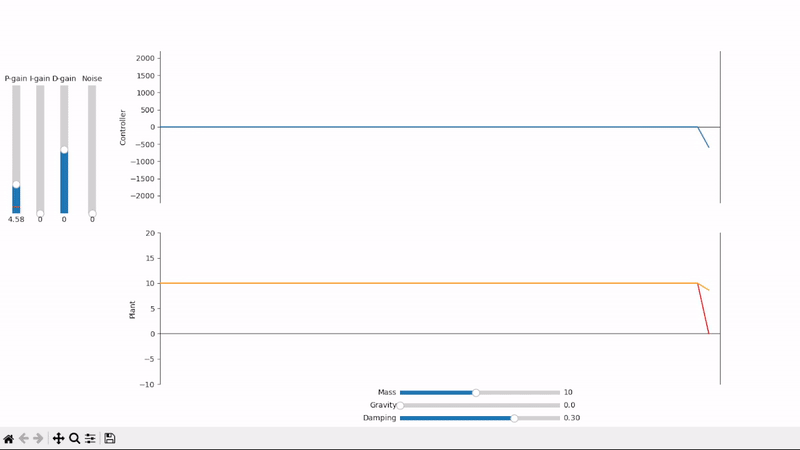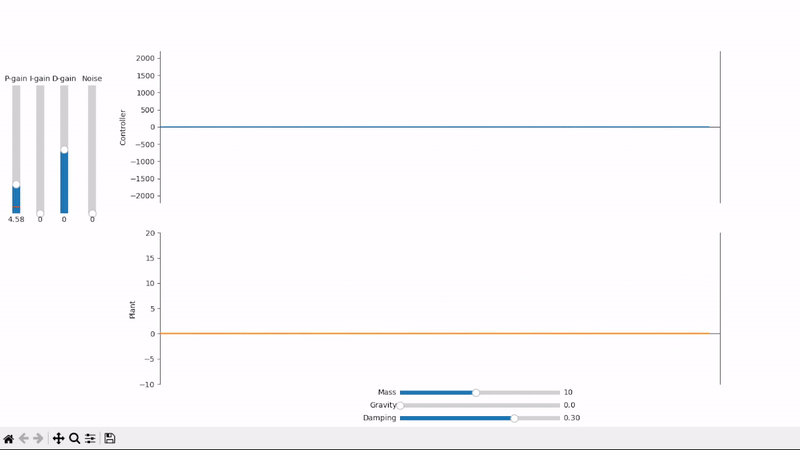
Increasing the proportional gain speeds up the system's response to changes in setpoint
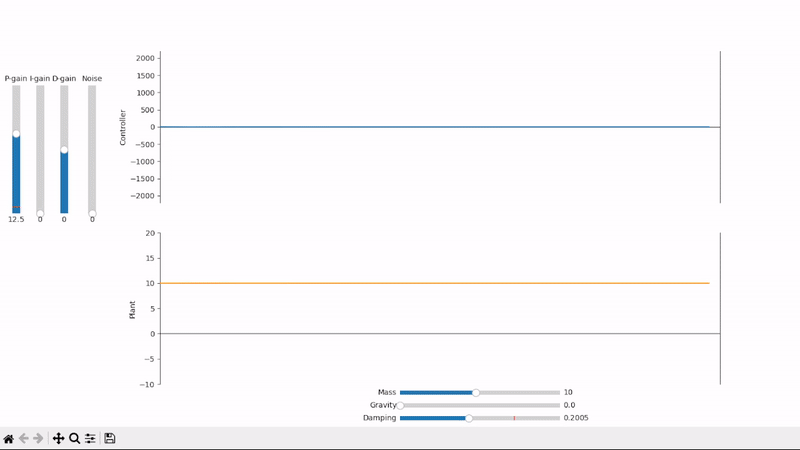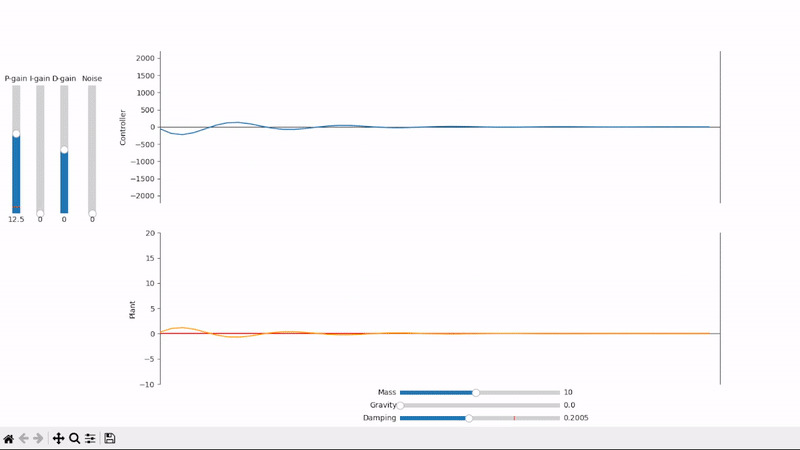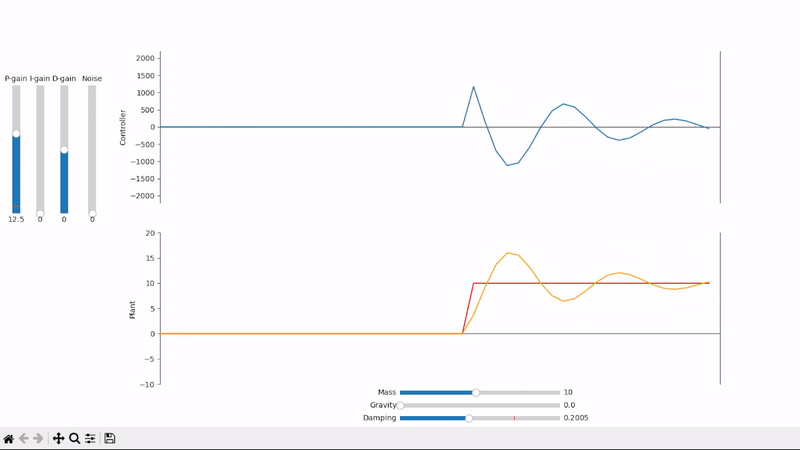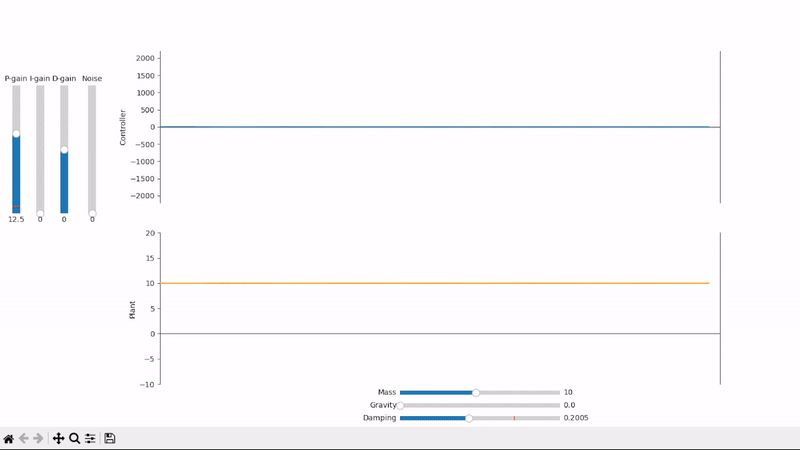
Too much proportional gain leads to overshoot and oscillations
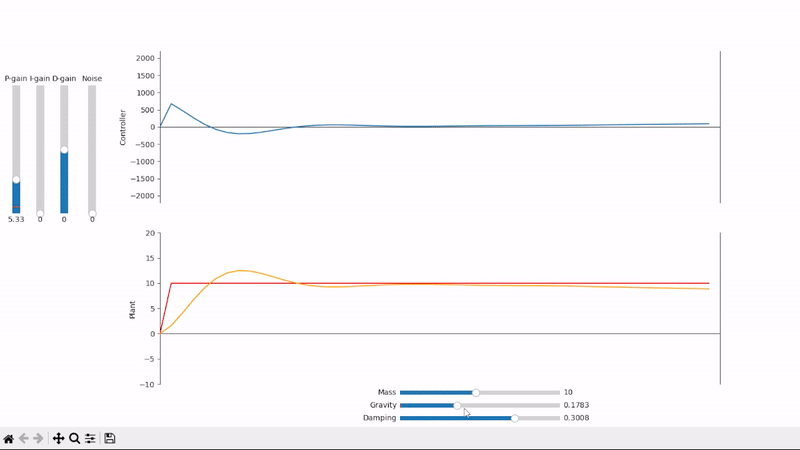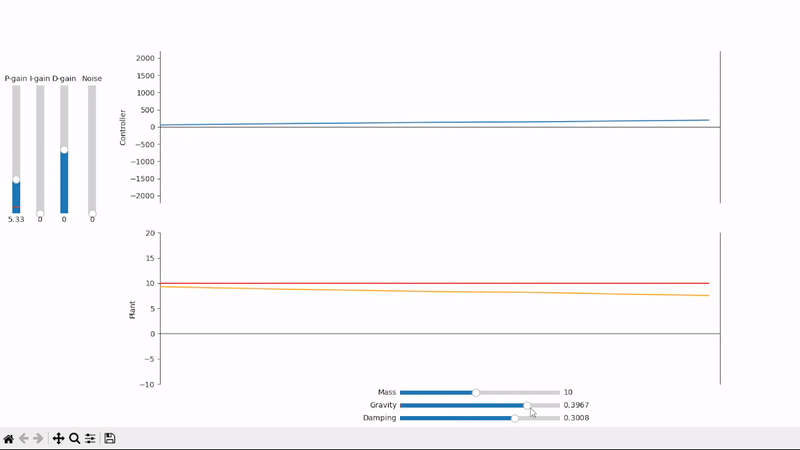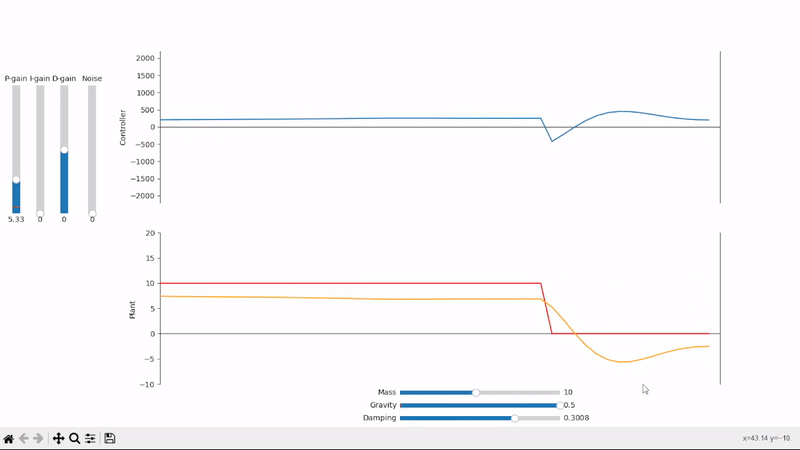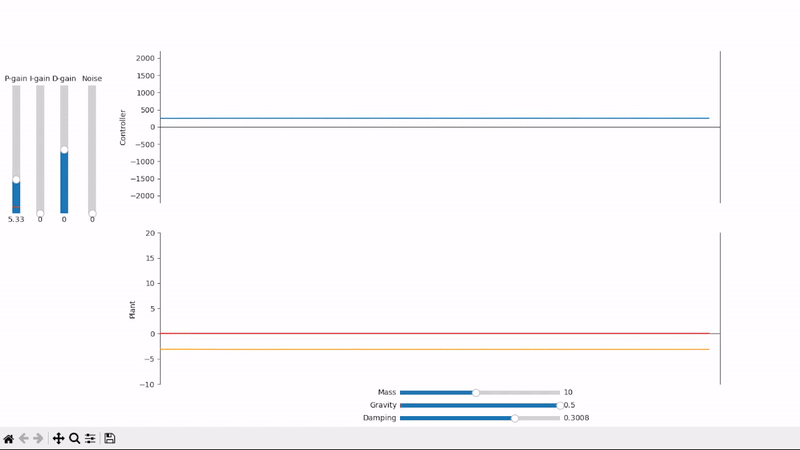
Proportional gain alone is not able to properly set the system under an external offsetting force
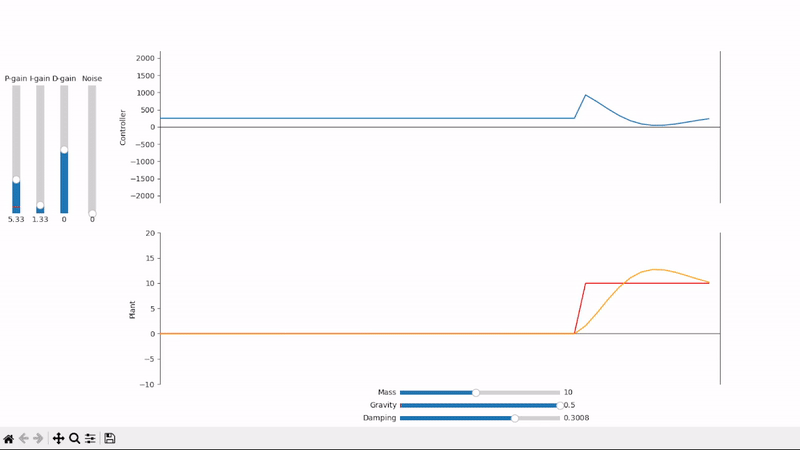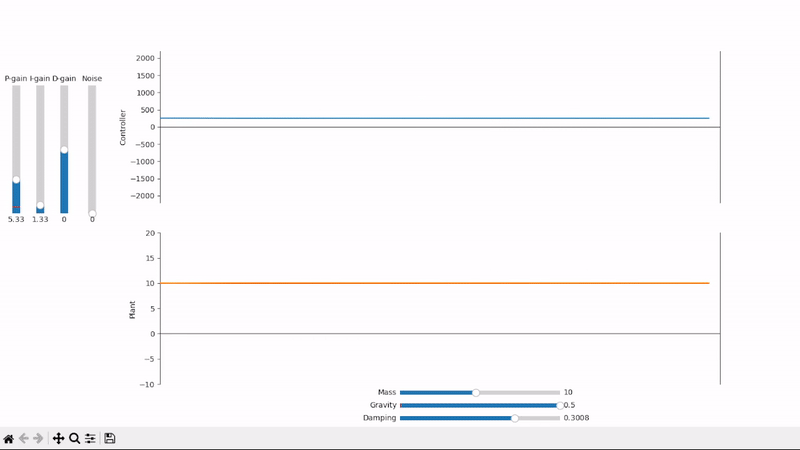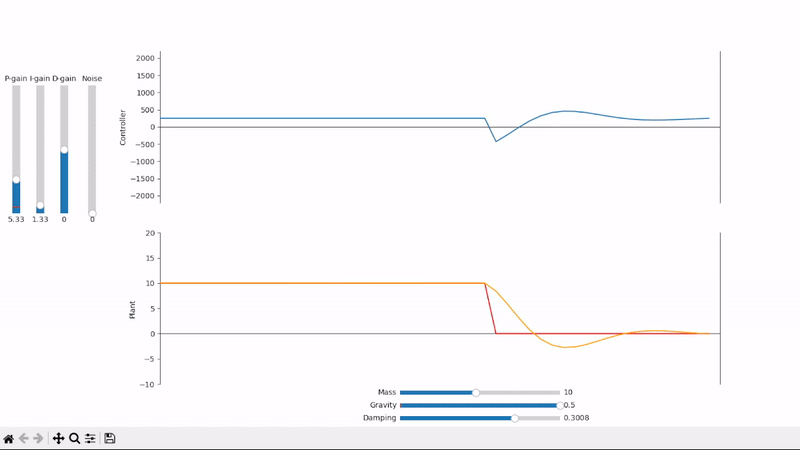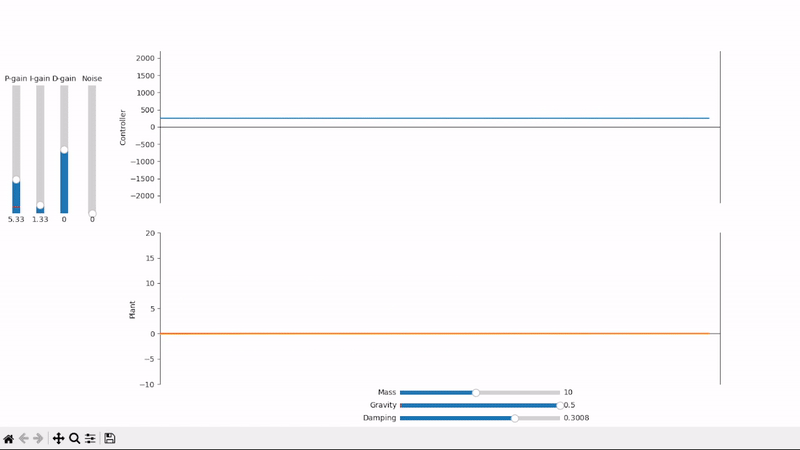
Integral gain compensates for constant offsets and long-term fluctuations
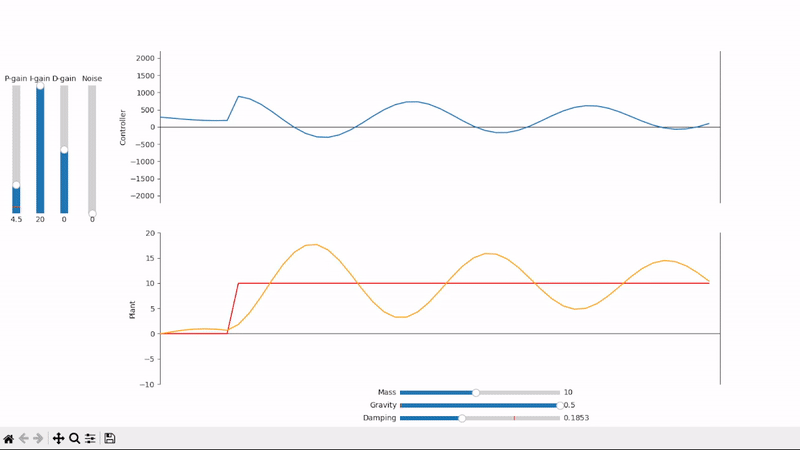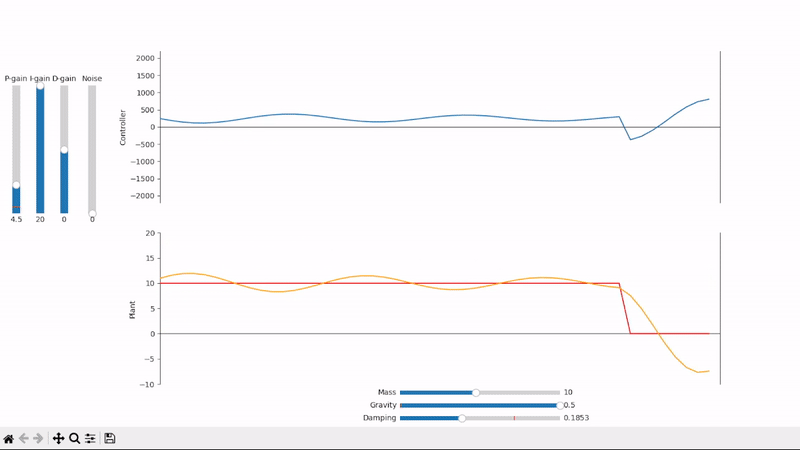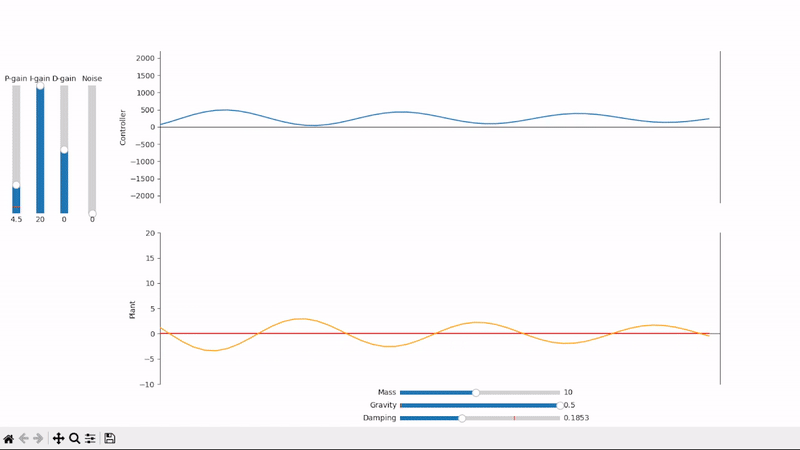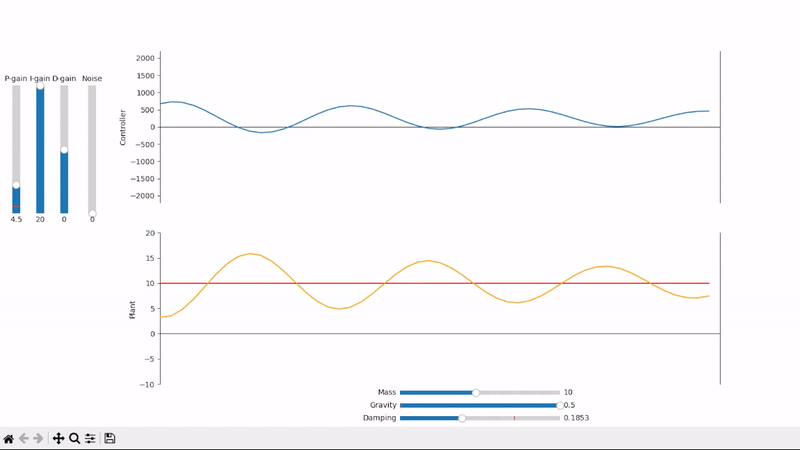
Excessive integral gain leads to system instability
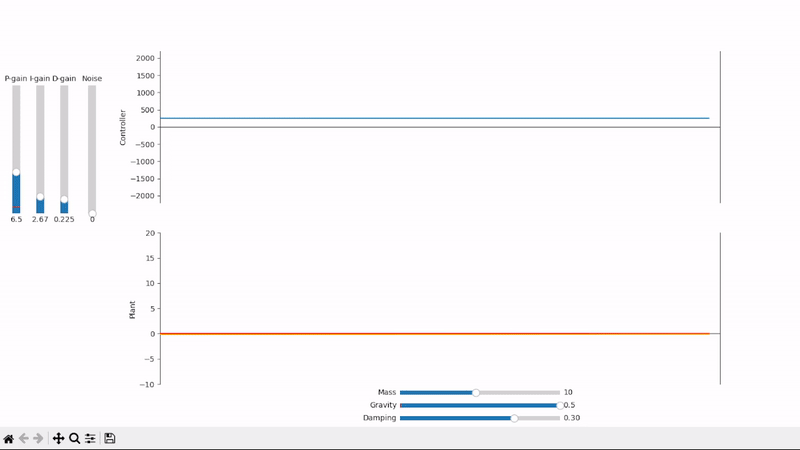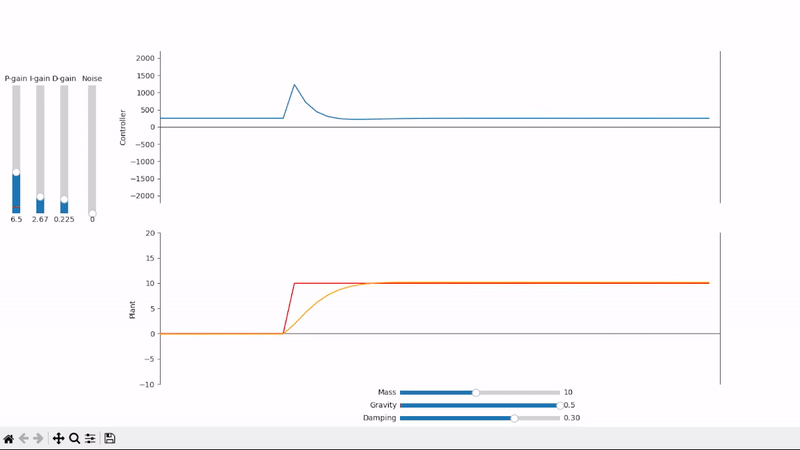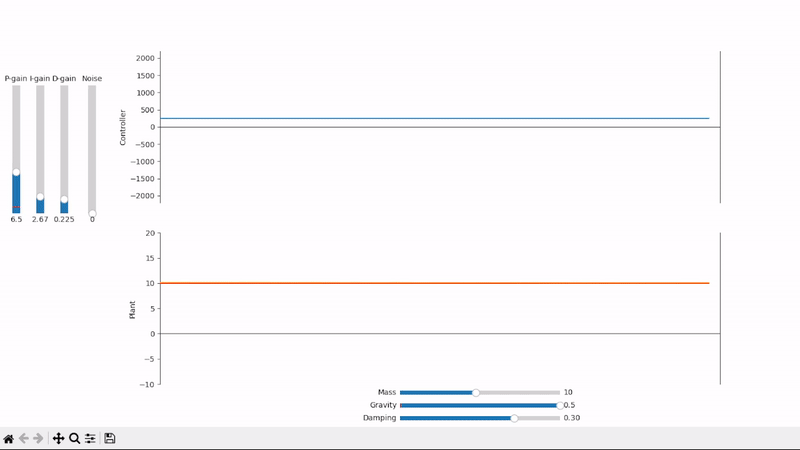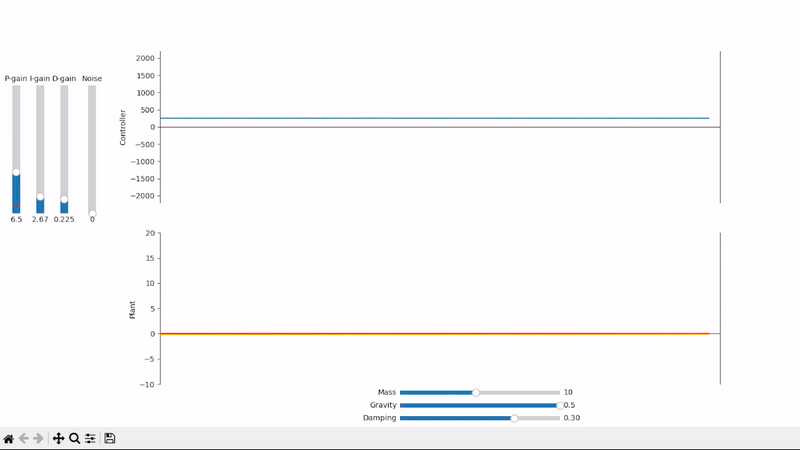
Derivative gain can help speed up the system's response to quick setpoint changes and reduce overshoot
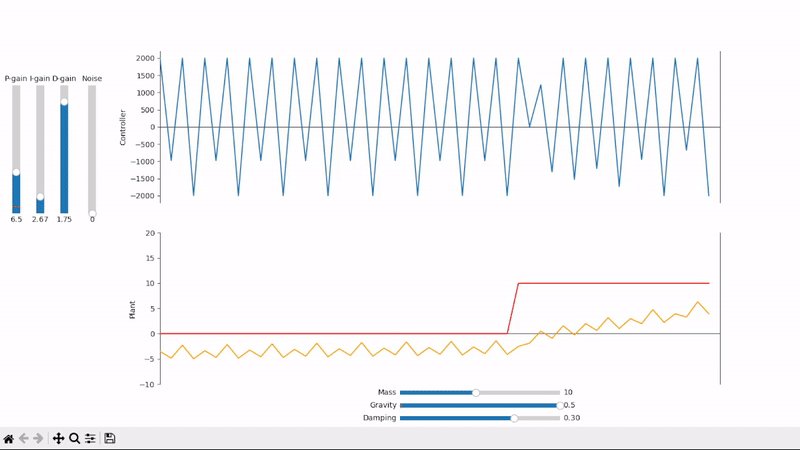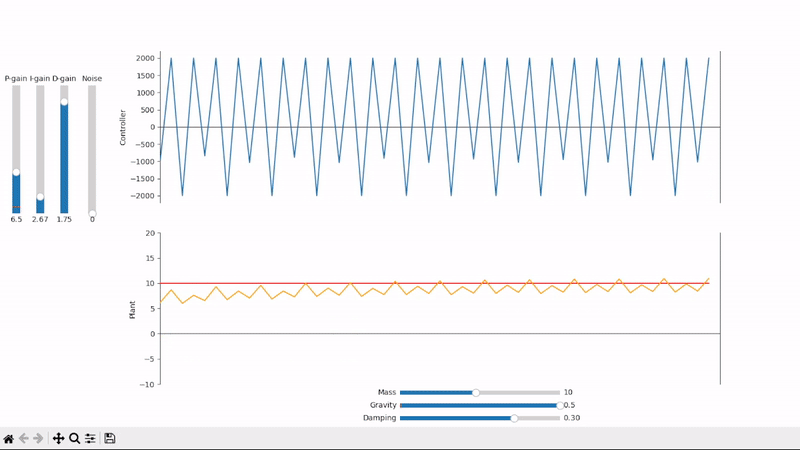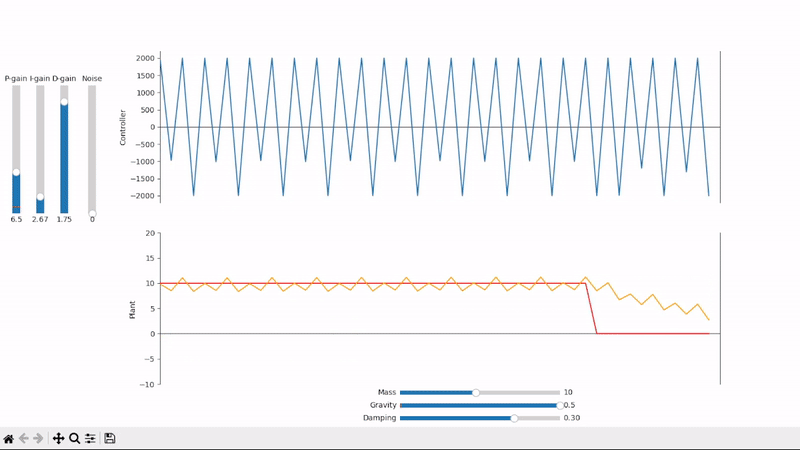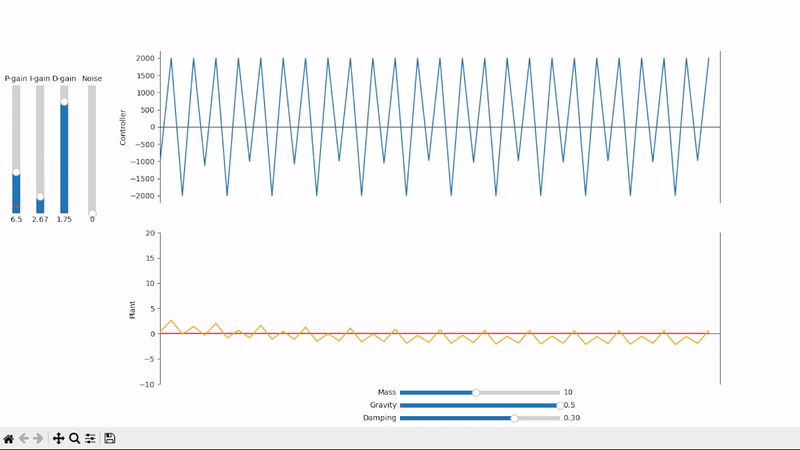
Excessive derivative gain leads to short period oscillations
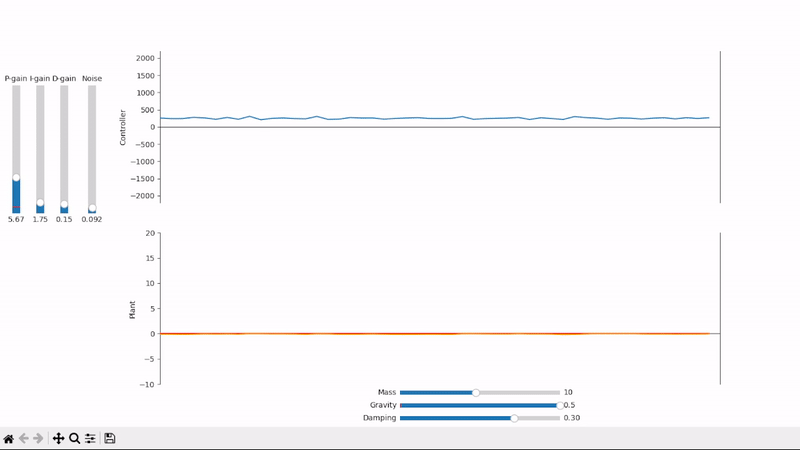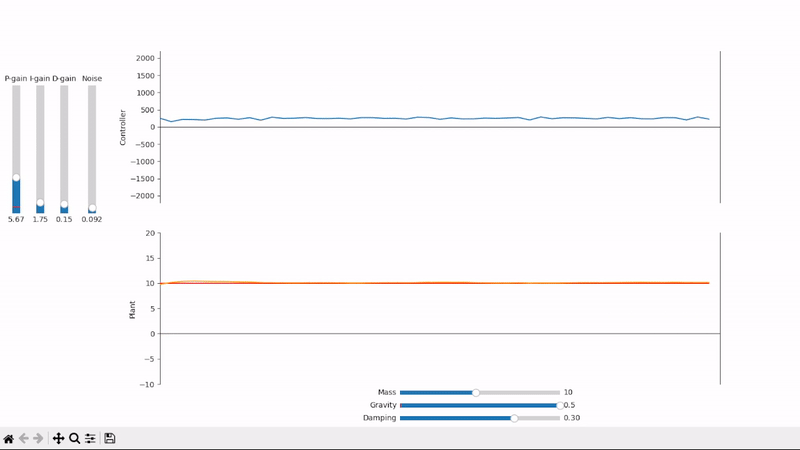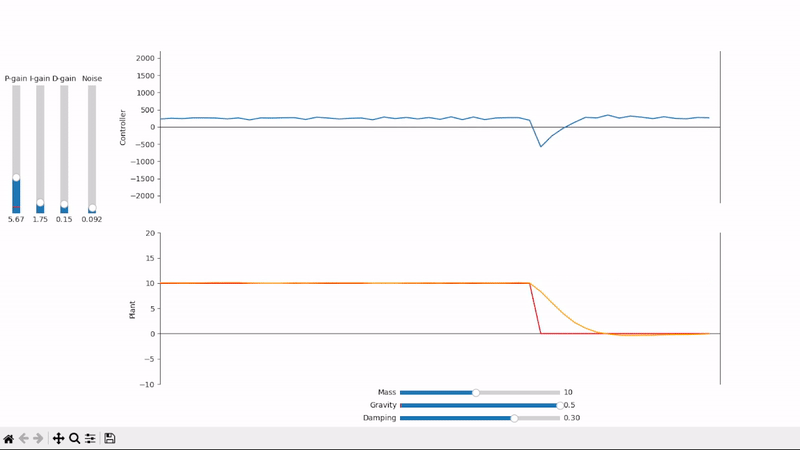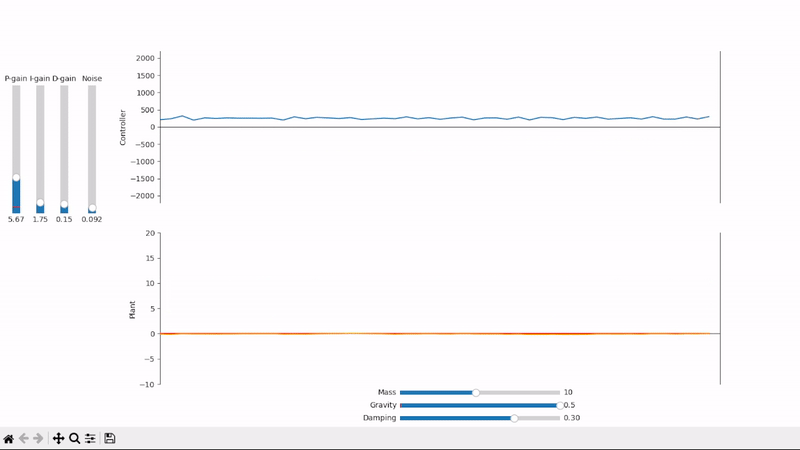
A well-tuned PID controller responds to changes as quickly as possible while avoiding excessive overshoot and remains stable when controlling noisy and highly dynamic systems
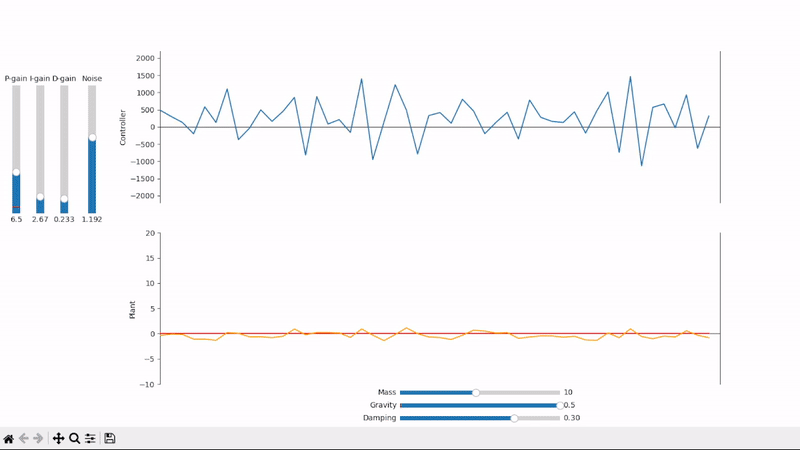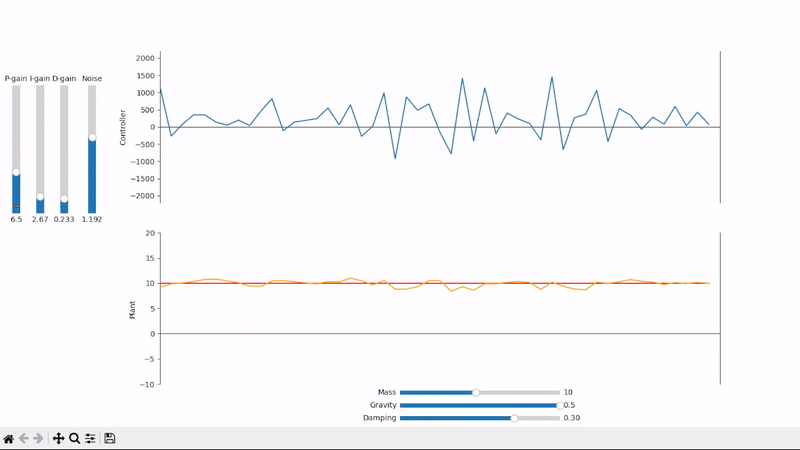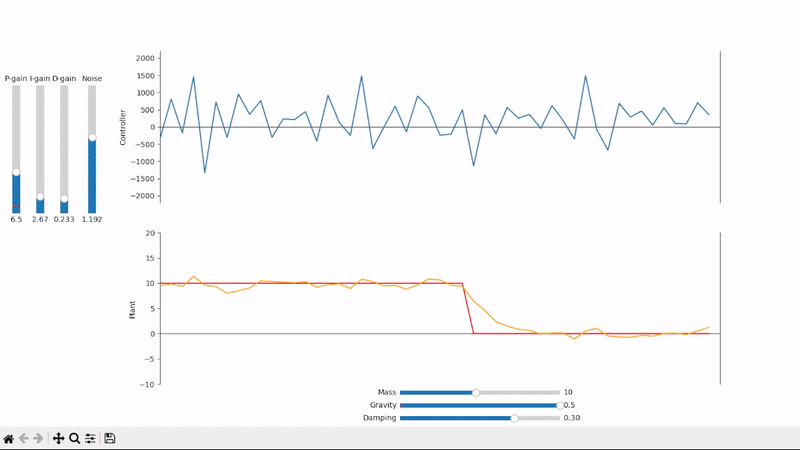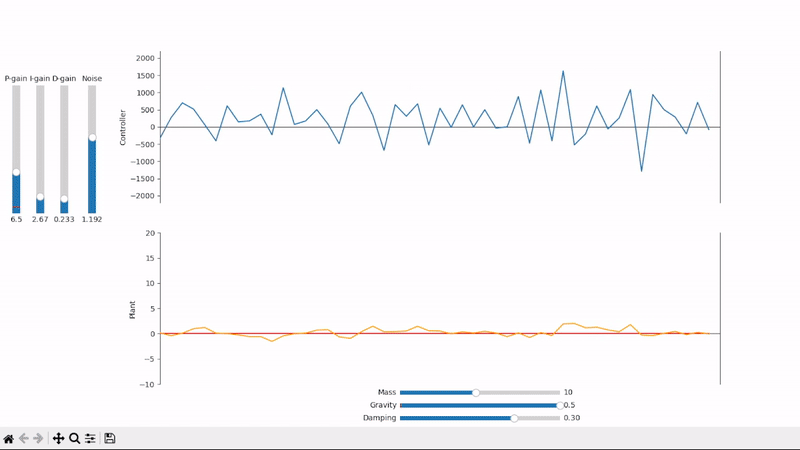
Derivative gain can amplify noise to unacceptable levels